Biology 140, Test 2 Review
1. What is the difference between a species fundamental niche and realized niche? How does this relate to the competitive exclusion principle?
2. Abiotic Factors: How do each of the following affect animals?
temperature light wind currents waves
3. Which of the following is most likely a tertiary consumer?
a. A fox eating a rabbit
b. A deer eating leaves
c. A shark eating a fish-eating seal
d. A bird eating a grasshopper
e. None of the above
4. What are some limitations on the growth of a population?
5. Which of the following sequences correctly illustrates a food chain?
a. Diatoms-fish-human-insects
b. Fish-insect larvae-algae-human
c. Insect larvae-algae-fish-human
d. Algae-mayfly larvae-trout-human
e. Damselfly larvae-trout-algae-grizzly bear
6. In most food chains:
a. There are fewer individuals at the top predator level than at the second trophic level
b. There is less usable energy at the herbivore level than at the carnivore level
c. There are few individuals at the decomposer level
d. There is more usable energy at the carnivore level
e. None of the above
7. Which level of a food chain will have the greatest amount of biomass? Producers
8. Does competition usually take place between two different species? No, one will change to their realized niche, move or die
9. Why do mountain lions need to have a larger home range than deer? Higher on the food chain
10. How do predators affect the population of their prey? What is a keystone predator?
11. Biotic Factors: Be able to define and identify examples of
parasitism mutualism commensalism predation competition
12. How did DDT harm the population of Bald Eagles? Biomagnification, thin egg shells
13. Explain why broad-spectrum pesticides do not control pests long-term.
14. What are3 alternative pest-control measures that could be taken? see notes
15. If broad-spectrum pesticides kill the pest and their predators, the pest population will come back in greater numbers than before. Why? No population control
16. Define herbivorous, omnivorous, carnivorous.
17. Vocabulary
niche producer tertiary consumer
carrying capacity primary consumer
limiting factor secondary consumer
range of tolerance decomposer scavenger
|
|
How many grams of algae biomass are needed to support one gram of this grizzly bear? The bear is eating salmon who feed as secondary consumers. 1000 grams |
|
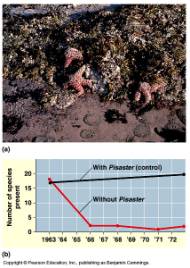
Explain why this intertidal area has greater diversity with the seastar Pisaster than without it. Pisaster controls the mussel population, which can out-compete other species if not controlled
|
|
|
|
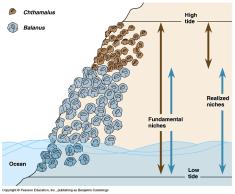
Why doesn't the barnacle Chthamalus occupy its full niche in the presence of the barnacle Balanus? They can't share the same niche due to the competitive exclusion principle. Balanus outcompetes Chthamulus at lower intertidal areas, so Chthamulus occupies only higher intertidal areas when Balanus is present. Balanus can not survive in the higher intertidal region. |